Many believe taste and odor mainly rely on food ingredients, but environmental factors and individual health are just as influential. Pollution, mold, and odors from pets or garbage can dull your senses or cause discomfort, while medical conditions like allergies or illness may impair perception. Good oral hygiene, healthy lifestyle choices, and managing environmental pollutants truly matter for maintaining your sensory health. To protect and enhance your senses, it’s important to understand what sources are genuine and how to address them; explore more to learn how.
Key Takeaways
- Perception of taste and smell is influenced by neural processing and individual biological differences, not just surface senses.
- Environmental odors and pollution can dull or mask natural flavors, affecting sensory perception.
- Medical conditions, medications, and aging can impair taste and smell, but lifestyle choices may mitigate decline.
- Food ingredients and additives shape flavor and aroma, but external factors like storage and exposure also play critical roles.
- Proper hygiene, ventilation, and environmental management support sensory health by reducing contaminants and odor interference.
Common Myths About Taste and Smell Origins

Many people assume that taste and smell originate solely from the tongue and nose, but this isn’t entirely true. Your perception of flavor is influenced by more than just these sensory organs. Food processing techniques can alter how your body perceives taste and aroma, but genetic factors also play a significant role. Some individuals are born with heightened sensitivity to certain flavors or smells, while others may have diminished senses due to genetic variations. For example, genetic differences can affect the number and function of taste buds or olfactory receptors, shaping your unique flavor profile. These biological factors help explain why people experience taste and odor so differently, regardless of external factors. Understanding this helps dispel the myth that taste and smell are purely environmental or surface-level senses. Additionally, research shows that sensory perception can be affected by neural pathways and brain processing, which further influences individual differences in flavor experiences.
The Role of Food Ingredients Versus Environmental Factors

While the ingredients in your food directly influence its flavor and aroma, environmental factors also play a crucial role in shaping your sensory experience. These factors can modify how you perceive taste and odor, often through processes like sensory adaptation. For example, you might notice a lingering aftertaste or diminished sensitivity after exposure to strong flavors. Consider these aspects:
- Food additive effects can alter perception, sometimes masking or enhancing certain flavors.
- Environmental odors, such as cooking smells, can influence your taste responses by competing or synergizing with food aromas.
- Sensory adaptation causes your senses to become less responsive over time, affecting how you perceive subsequent flavors.
- Robotics integration in food production and packaging can also impact sensory experiences by influencing texture and freshness perceptions.
Understanding these influences helps clarify why your experience of taste and smell varies beyond just ingredients.
How Medical Conditions Can Influence Sensory Perception

Medical conditions can substantially alter how you perceive taste and smell, often disrupting your normal sensory perception. For example, conditions like sinus infections, allergies, or nasal polyps block odor pathways, dulling your sense of smell. Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s can impair how your brain interprets sensory signals, leading to changes in taste and odor perception. Medical conditions like diabetes or certain vitamin deficiencies can also affect sensory perception by damaging nerves or altering chemical balances. Medications might have side effects that diminish your ability to detect flavors or odors. Recognizing how a medical condition influences your senses is essential for understanding changes in taste and smell, helping you address underlying issues and improve your overall sensory experience.
The Impact of Oral Hygiene on Taste and Odor
Your oral hygiene habits directly influence your ability to taste and smell. Poor oral hygiene can lead to plaque buildup, bacteria, and bad breath, all of which impair taste perception. To maintain ideal sensory function, focus on these key practices:
- Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste to remove debris and bacteria.
- Flossing regularly to eliminate food particles between teeth.
- Visiting your dentist periodically for professional cleanings.
- Understanding the importance of contingency plans in managing oral health issues can prevent long-term sensory impairment.
These steps help keep your mouth healthy, preventing infections and coatings that dull your taste buds. When your oral hygiene is well-maintained, your taste perception remains sharp, allowing you to enjoy flavors more fully. Good oral hygiene isn’t just about aesthetics—it’s essential for preserving your senses of taste and odor.
Environmental Pollution and Its Effect on Sensory Experiences
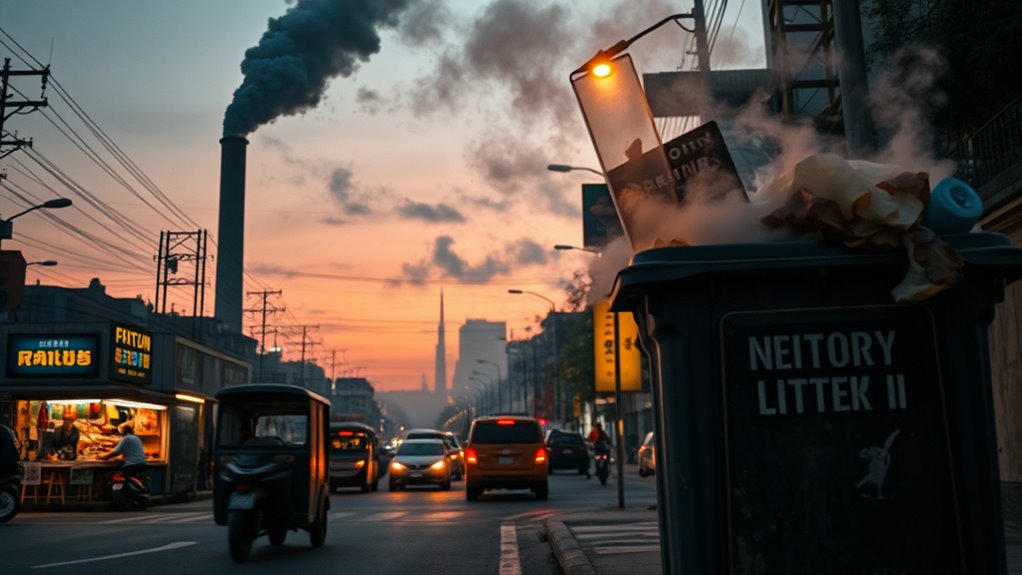

Environmental pollution can considerably alter your sense of taste and smell, making everyday experiences less clear. Contaminants in the air and water can introduce new odors or dull familiar ones, affecting your perception. Understanding how pollution impacts your sensory environment helps you recognize and address these subtle changes. Additionally, exposure to certain pollutants can weaken the cybersecurity of connected devices, potentially leading to data breaches or unauthorized access, which underscores the importance of maintaining robust security measures in our increasingly digital world.
Pollution’s Impact on Taste
Pollution can substantially alter the taste of food and water, often making them unpleasant or even unsafe to consume. Poor air quality introduces airborne pollutants that settle on produce and water surfaces, impacting flavor. Water contamination, from industrial runoff or wastewater, can infuse water with chemicals that change its taste. Here’s what you should know:
- Harmful chemicals like pesticides or heavy metals can create metallic or bitter flavors.
- Contaminants such as algae or bacteria produce foul tastes, affecting water and food.
- Airborne pollutants can deposit onto crops, imparting chemical or smoky notes.
These factors directly influence your sensory experience, making it vital to consider pollution’s role in taste alterations and the importance of clean air and water for safe consumption.
Odor Pollution and Health
Airborne odors from pollution can considerably impact health by affecting your senses and signaling potential dangers. Poor air quality often carries harmful pollutants that amplify odor detection, making you more sensitive to unpleasant smells. Chronic exposure to polluted air can lead to respiratory issues, headaches, or fatigue, as your nose and senses work overtime to detect harmful substances. Odor pollution can mask or distort natural scents, reducing your ability to recognize dangerous leaks or environmental hazards. It’s crucial to understand how air quality influences odor perception because heightened sensitivity may indicate underlying health risks. By paying attention to changes in odor detection, you can better assess environmental dangers and take steps to protect your health from the adverse effects of odor pollution. Additionally, understanding the role of synthetic wigs and styling techniques can help prevent exposure to potentially harmful chemicals during Halloween preparations.
Contaminants Alter Sensory Perception
Contaminants in the environment can profoundly alter how your senses perceive the world around you. Airborne toxins and cosmetic chemicals can distort taste and smell, making everyday experiences unfamiliar or unpleasant. These pollutants interfere with sensory receptors, leading to misperceptions or diminished sensitivity. Specifically, you might notice:
- Altered taste perception due to exposure to certain cosmetic chemicals that block or stimulate taste buds.
- Disrupted smell recognition caused by airborne toxins that damage or numb olfactory receptors.
- Increased sensory fatigue from constant exposure to airborne pollutants, dulling your overall sensory acuity.
- Environmental pollution can also impact car engine tuning, where contaminants can affect sensor performance and vehicle response.
Understanding these influences helps you recognize that pollution not only affects health but also changes how you experience your environment on a fundamental level.
The Importance of Hydration for Maintaining Taste and Smell

Staying well-hydrated is essential for preserving your sense of taste and smell, as dehydration can dull these senses and affect your ability to enjoy food and detect odors. Hydration importance can’t be overstated; when you’re dehydrated, mucus membranes in your mouth and nasal passages become dry, impairing their ability to transmit sensory signals. Adequate water intake keeps these membranes moist and functioning properly, supporting ideal sensory perception. Drinking enough water also helps flush out toxins that could interfere with your senses. If you notice a decline in taste or smell, consider your hydration levels first. Maintaining consistent water intake is a simple yet effective way to support your body’s sensory functions and ensure you experience flavors and aromas fully. Additionally, understanding the role of contrast ratio in visual perception highlights how proper hydration can influence sensory experiences beyond taste and smell.
Dietary Choices That Can Enhance or Diminish Sensory Function

Your dietary choices directly influence your ability to perceive tastes and odors. Consuming nutrient-rich foods supports sensory health, while deficiencies can impair it. To enhance your senses, consider these strategies:
- Incorporate nutritional supplements like zinc or omega-3s, which may bolster sensory function.
- Practice sensory training by regularly focusing on different flavors and aromas to sharpen perception.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins to provide essential vitamins and antioxidants that protect sensory cells.
- Incorporate natural materials such as linen or wood in your environment, which can subtly influence sensory comfort and perception.
Avoid excessive alcohol and processed foods, as they can diminish sensory sensitivity over time. Your diet plays a essential role; making mindful choices can preserve or even improve your taste and smell acuity.
The Significance of Aging in Taste and Odor Changes

As you age, your sense of taste and smell naturally decline, affecting how you experience flavors and odors. This happens because taste buds become less numerous and less sensitive, and odor receptors gradually deteriorate. Understanding these changes helps you adapt and maintain your sensory enjoyment over time. Additionally, sensory decline can be influenced by lifestyle factors and overall health, emphasizing the importance of a healthy diet and environment to support your senses.
Age-Related Sensory Decline
Aging naturally affects your senses of taste and smell, often leading to noticeable declines over time. This sensory adaptation can diminish how vividly you perceive flavors and odors. It’s important to recognize that this decline isn’t solely due to aging but also influenced by factors like diet and environmental exposure. Here’s what matters:
- Sensory decline varies based on genetics, lifestyle, and health conditions.
- Dietary influence plays a role, as certain nutrients support sensory health.
- Regular exposure to diverse flavors can help maintain sensitivity despite aging.
- Proper storage and handling techniques for juices and other foods can help preserve their aroma and flavor, which is especially beneficial as sensory perception diminishes with age.
Understanding these factors helps you adapt your habits and maintain a richer sensory experience. While aging may reduce your baseline perception, proactive choices can slow the decline and keep your senses sharper longer.
Changes in Taste Buds
Changes in taste buds are a key factor in how your sense of taste evolves with age. As you get older, your taste buds undergo slower regeneration, which means they don’t renew as quickly as they once did. This reduced taste bud regeneration decreases the number of functioning taste receptors, leading to altered flavor perception. You might notice that foods taste blander or less vibrant than before. This change isn’t just about aging; it’s also influenced by other factors like health and habits. While your taste buds continue to regenerate, their decreased renewal affects your overall taste sensitivity. Understanding this process helps you realize that changes in flavor perception are natural, and they don’t necessarily mean your taste experience is diminishing entirely.
Odor Receptor Deterioration
While your taste buds gradually become less responsive over time, your sense of smell also faces similar challenges. Odor receptor deterioration is a key factor in age-related smell decline, driven by neural degeneration that affects receptor sensitivity. As you age, the following changes occur:
- Neural degeneration reduces the number of functioning olfactory neurons, decreasing overall sensitivity.
- Receptor sensitivity diminishes, making it harder to detect faint odors.
- The regeneration rate of olfactory receptors slows, prolonging recovery from damage or infection.
These combined effects cause a noticeable decline in your ability to perceive odors accurately. Understanding this deterioration highlights how aging impacts sensory functions, emphasizing the importance of maintaining overall neural health to preserve your sense of smell over time.
Recognizing Genuine Sources of Unpleasant Odors in Your Environment
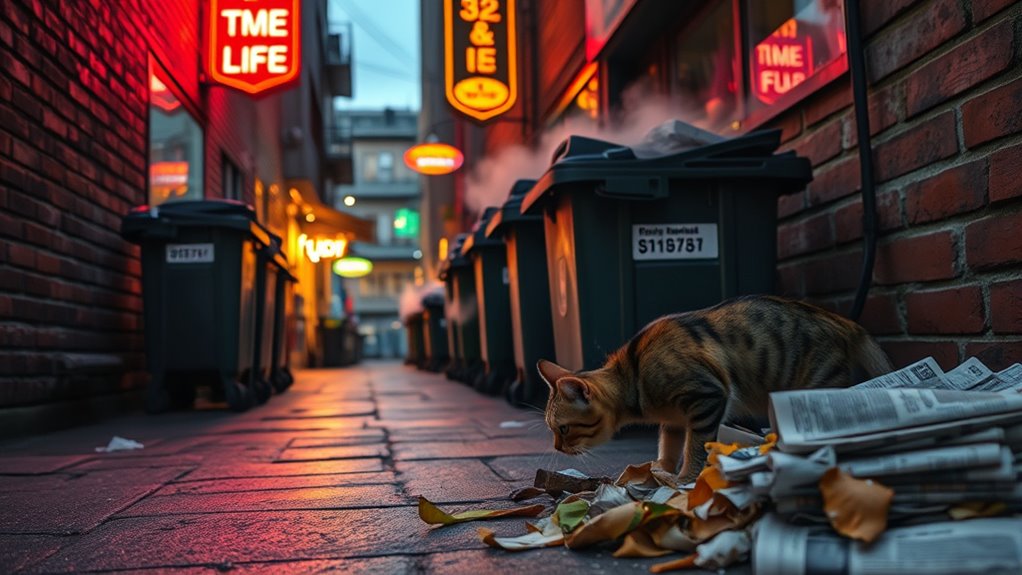

Recognizing genuine sources of unpleasant odors in your environment requires careful observation and a keen sense of smell. Start by identifying consistent smells rather than temporary ones. Indoor air often carries hidden sources like pet odors, mold, or garbage. Pet odors can linger on furniture, carpets, or bedding, making the space feel stuffy. Use your nose to pinpoint areas where smells are strongest.
| Suspected Source | Common Indicators |
|---|---|
| Pet odors | Faint smell on furniture or pet bedding |
| Mold | Musty smell on walls or ceilings |
| Garbage | Strong, persistent smell near trash bins |
| Indoor air | Lingering odors without obvious cause |
Practical Steps to Support Your Sensory Health

To support your sensory health effectively, start by maintaining a clean and clutter-free environment, as this reduces the buildup of dust, mold, and other irritants that can impair your senses. Incorporate daily routines like sensory training exercises to strengthen your olfactory and taste responses. Additionally, consider aroma therapy using essential oils like eucalyptus or peppermint, which can stimulate and refresh your senses. To optimize your approach, follow these steps:
- Engage in regular sensory training exercises, such as identifying different scents or flavors.
- Use aroma therapy strategically to enhance sensory stimulation and promote relaxation.
- Keep your environment clean and well-ventilated to prevent irritant buildup that dulls your senses.
These practices can help sharpen your sensory perception and support long-term health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Certain Medications Permanently Alter Taste and Smell Perceptions?
Certain medications can temporarily alter your taste and smell perceptions due to medication side effects, but these changes generally aren’t permanent. Sensory adaptation might cause your senses to adjust over time, making flavors or odors seem different. However, in rare cases, prolonged use of specific drugs could lead to lasting changes. Always discuss potential side effects with your doctor, especially if you notice persistent changes in your senses.
How Do Cultural Differences Influence Taste and Odor Preferences?
Cultural influences shape your taste and odor preferences by exposing you to diverse culinary traditions that develop your palate over time. You naturally prefer flavors and aromas familiar from your cultural background, which influences your reactions to new foods. These preferences are deeply rooted in social practices, regional ingredients, and cooking methods, making your taste unique. Embracing different culinary traditions broadens your sensory experiences and enhances your appreciation for global flavors.
Are There Genetic Factors That Determine Sensory Sensitivity?
Yes, genetic factors influence your sensory sensitivity, affecting how you perceive taste and odor. Your genetic predispositions determine your sensory thresholds, meaning some people are more sensitive to certain flavors or smells than others. This variation is natural and can explain why you might find certain tastes intense or barely noticeable. Understanding these genetic influences helps clarify individual differences and highlights the biological basis behind sensory experiences.
What Role Do Psychological Factors Play in Perceiving Odors and Flavors?
Think of your mind as a filter that colors your perception, like tinted glasses. Psychological factors, such as sensory bias and emotional associations, shape how you perceive odors and flavors. If you associate a smell with a happy memory, it will seem more pleasant, even if the scent is neutral. Your emotions and biases actively influence your sensory experience, making perception a personal story rather than just a chemical detection.
Can Sensory Training Improve Diminished Taste and Smell Functions?
Yes, sensory training can improve diminished taste and smell functions. Engaging in taste training and smell rehabilitation exercises helps stimulate your olfactory and taste receptors, encouraging recovery. You can practice identifying different flavors and odors daily to enhance your senses. Consistent effort in these activities can lead to noticeable improvements, especially if done under professional guidance. Don’t give up—your senses can often be retrained with dedicated practice.
Conclusion
Think of your senses as a delicate garden—you need to tend to each plant to keep it thriving. By understanding what truly influences your taste and smell, you can nurture your sensory health and avoid wandering down false paths. Stay aware of environmental factors, medical conditions, and your habits. With mindful care, you’ll enjoy a vibrant, flavorful world—like a well-tended garden bursting with colors and aromas, inviting you to savor every moment.









