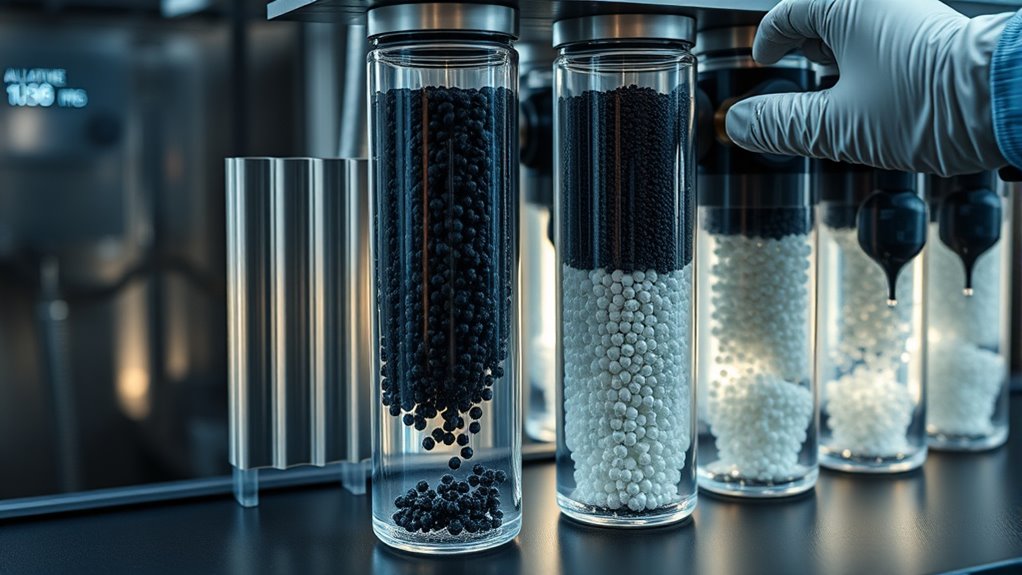
To design an effective filter system for chloramine removal, start by combining catalytic reduction media to break down chloramine molecules early in the process, followed by activated carbon to adsorb residual contaminants. Make certain your filter allows sufficient contact time and maintains proper flow rates for maximum efficiency. Regularly replace saturated media to keep performance high. If you keep exploring, you’ll learn how to optimize your system for the cleanest, safest water possible.
Key Takeaways
- Incorporate catalytic reduction media early to convert chloramine into harmless compounds before adsorption.
- Use high-quality activated carbon specifically designed for chloramine removal to maximize adsorption efficiency.
- Optimize flow rate and contact time to ensure sufficient interaction between water and filter media.
- Design multi-layer filters combining catalytic media and activated carbon for comprehensive chloramine removal.
- Schedule regular media replacement and maintenance to sustain filter performance and water quality.

Are you aware that chloramine, a common disinfectant in municipal water supplies, can pose health risks and cause unpleasant tastes and odors? If you’re concerned about removing chloramine from your water, designing an effective filter system is essential. The key to successful removal lies in understanding how certain filtration media work, particularly activated carbon and catalytic reduction methods.
Activated carbon is widely recognized as a highly effective medium for removing chloramine. Its porous structure provides a large surface area, allowing it to adsorb contaminants efficiently. When water flows through an activated carbon filter, chloramine molecules are attracted to and bond with the surface of the carbon particles. This process considerably reduces chloramine levels, improving water taste and odor while minimizing health risks associated with residual disinfectants. To maximize effectiveness, you should select high-quality activated carbon specifically treated or designed for chloramine removal, as not all carbon types perform equally.
However, relying solely on activated carbon isn’t always enough. Chloramine is more resistant than chlorine alone, so incorporating catalytic reduction can enhance your filter’s performance. Catalytic reduction involves using specialized catalysts—often coated onto media like carbon or other substrates—that facilitate chemical reactions transforming chloramine into harmless compounds such as nitrogen gas and chloride ions. This process effectively neutralizes chloramine, making it easier for the filter media to remove residual particles. A catalytic reduction stage can be integrated into your filter system either before or alongside activated carbon, creating a multi-layered approach that guarantees more complete removal.
Designing your filter system requires careful consideration of flow rate, contact time, and media placement. You want water to pass slowly enough through the activated carbon to maximize adsorption, but not so slowly that flow becomes impractical. Incorporating catalytic reduction early in the process allows for the breakdown of chloramine molecules before they reach the activated carbon, boosting overall efficiency. Additionally, regular maintenance and media replacement are vital, as saturated activated carbon becomes less effective over time. Using a combination of activated carbon and catalytic reduction media—either in a single cartridge or staged filters—provides a thorough solution.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Often Should I Replace the Filter Media?
You should replace your filter media every 6 to 12 months, depending on your filter’s lifespan and usage. Regularly check your replacement schedule and monitor water quality to guarantee maximum chloramine removal. If you notice a decrease in water flow or taste changes, it’s a sign to change the filter sooner. Following the recommended replacement schedule helps maintain filter efficiency and keeps your water clean and safe.
Can I Use the Same Filter for Chloramine and Chlorine Removal?
You can’t use the same filter for chloramine and chlorine removal because of filter compatibility and chemical interactions. Chloramine is more stable than chlorine, so filters designed for chlorine might not effectively eliminate chloramine. Using a filter not specifically rated for chloramine can lead to reduced effectiveness and potential health risks. Always choose a filter tested and certified for chloramine removal to ensure safe and efficient water treatment.
What Are the Signs My Filter System Needs Maintenance?
Think of your filter system like a car; if you ignore regular check-ups, performance drops. Signs you need filter maintenance include reduced water flow, strange tastes or odors, or visible clogging. Performance indicators like increased chloramine levels downstream or frequent filter replacements also signal it’s time for a tune-up. Ignoring these signs can lead to less effective filtration, so stay vigilant to keep your system running smoothly and your water clean.
Is There Any Health Risk if Chloramine Isn’t Fully Removed?
If chloramine isn’t fully eliminated, you could face health concerns from ongoing chemical exposure, which may cause skin irritation, respiratory issues, or other health problems over time. Incomplete removal increases your risk of ingesting or coming into contact with harmful chemicals. To stay safe, make certain your filter system effectively removes chloramine, and test your water regularly for residual chemicals. Proper maintenance helps protect your health from potential risks associated with chemical exposure.
How Does Water Temperature Affect Filter Performance?
Water temperature impacts filter efficiency because higher temperatures can speed up chemical reactions, but they may also reduce the filter material’s effectiveness over time. Conversely, lower temperatures might slow down chloramine removal processes, making the filter less efficient. You should monitor temperature conditions regularly and choose a filter system designed to perform well within your typical water temperature range, ensuring peak chloramine removal and water quality.
Conclusion
Now that you know how to design an effective filter system for chloramine removal, you’re equipped to improve your water quality considerably. Remember, choosing the right filter media and maintaining it properly are key to success. Don’t settle for subpar water—aren’t your health and well-being worth the effort? By staying proactive and informed, you ensure clean, safe water for you and your family every day.